This post will be a comprehensive list – in one place – of the prescription medications and vitamins that may be prescribed for our loved ones suffering from dementias and Alzheimer’s Disease.
My main purpose in doing this is so that caregivers, as medical advocates for our loved ones, have the information needed about the common medications and vitamins used to treat the symptoms of these diseases.
Currently there is a lot of information on the internet about these, but it’s so scattered and oftentimes so clinically-written that it’s impossible to pull it all together and make wise decisions as to accepting or rejecting medication proposals from primary care physicians and psychiatrists.
And the preceding paragraph has some information caregivers need to know, exercise, and require for their loved ones.
First, both a primary care physician and a psychiatrist need to be involved in medical care for our loved ones. One of the first requests that should be made to the primary care physician after a dementias and/or Alzheimer Disease diagnoses should be a referral to a geriatric psychiatrist.
The reason caregivers need to do this is because geriatric psychiatrists specialize in treating elderly patients and they also have access to the latest research in the treatment of the symptoms of dementias and Alzheimer’s Disease.
Primary care physicians are not specialists. This includes internists. They know a little bit about a lot of things, which is exactly what they were trained for (and that’s not a bad thing), but they don’t have the time nor the resources to be experts in any one thing.
Therefore, a geriatric psychiatrist is an absolute necessity to ensure our loved ones get the best care possible to treat the symptoms of these diseases.
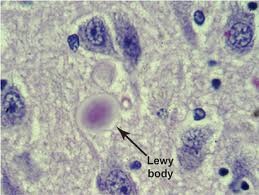
Second, you have the right to refuse medication. For example, one of the medications that Mom’s primary care physician wanted to give her as the Lewy Body dementia symptoms worsened was Abilify. No doubt you’ve all seen the commercials touting Abilify as a “booster” for use with anti-depressants to relieve chronic depression.
This is an “off-label” use of the drug. So is prescribing it for our loved ones with dementias and Alzheimer’s Disease (a lot of the mood and psychosis-managing drugs prescribed for people suffering from dementias and Alzheimer’s Disease are “off-label” uses of those drugs).
I did the homework on it before I filled the prescription. Ability was created to treat schizophrenia. That would have probably been okay, but then I saw the warning that “ABILIFY (aripiprazole) is not approved for the treatment of people with dementia-related psychosis.”
In addition, by then I knew Mom also had Lewy Body dementia in addition to vascular dementia and Alzheimer’s Disease and I knew about the increased neuroleptic sensitivity associated with Lewy Body dementia, so I didn’t fill the prescription.
 The first category of prescription medications is the cognitive enhancers. These drugs are designed to maintain mental health and may improve memory, awareness and the ability of our loved ones to go about their daily activities by boosting the function of existing neurotransmitters involved in memory and judgment in the brain. They will not reverse nor stop the neurological course of the diseases. They are:
The first category of prescription medications is the cognitive enhancers. These drugs are designed to maintain mental health and may improve memory, awareness and the ability of our loved ones to go about their daily activities by boosting the function of existing neurotransmitters involved in memory and judgment in the brain. They will not reverse nor stop the neurological course of the diseases. They are:
- Aricept – Approved for all stages of dementias and Alzheimer’s Disease, but most effective in mild to moderate stages
- Razadyne – Mild to moderate stages of dementias and Alzheimer’s Disease
- Excelon – Mild to moderate stages of dementias and Alzheimer’s Disease
- Namenda – Moderate to severe stages of dementias and Alzheimer’s Disease
The second category of prescription medications treats the mood and psychosis symptoms of dementias and Alzheimer’s Disease.
These medications need to be closely monitored and carefully dosed.
The optimal result of these medications is mood stabilization and no psychosis. If your loved ones are “knocked out” by this category of medications, the doses are too high. If your loved ones are “out of control,” the doses are too low. This is another reason you want a psychiatrist involved.
There are many possible combinations of this category of drugs. All the anti-psychotic drugs have possible side effects and extreme caution should be exercised, because of the high sensitivity to neuroleptics, in using these with our loved ones with Lewy Body dementia. Some of the most commonly-used medications are:
- SeroquelXR – anti-psychotic (possible side effects of neuroleptic sensitivity and tardive dyskinesia in Lewy Body dementia)
- Citalopram – anti-depressant
- Clonazepam – anti-anxiety
Anti-anxiety medications seem to be the most frequently mismanaged in this category of drugs. My advice is to advocate with our loved ones’ psychiatrists for low dosages and have them prescribe it to be taken as-needed instead of as part of the daily medication regimen.
The medication, Halcyon, by the way, should be avoided at all costs in people suffering from dementias and Alzheimer’s Disease. It really wreaks havoc and it has a very long half-life! The most likely place this would be given is during hospitalizations, so be sure to let all the hospital staff you come in contact with know that our loved ones should not be given Halcyon for anxiety and/or sleep.
 Vitamin supplements may be added to address some of the functioning difficulties brought on by dementias and Alzheimer’s Disease. In my personal experience, I really don’t believe they’re all that effective after the fact of diagnosis. However, we all should make sure we have plenty of this in our own diets now to protect ourselves.
Vitamin supplements may be added to address some of the functioning difficulties brought on by dementias and Alzheimer’s Disease. In my personal experience, I really don’t believe they’re all that effective after the fact of diagnosis. However, we all should make sure we have plenty of this in our own diets now to protect ourselves.
The most common are:
- Folic acid – helps memory and mental processing speed
- Vitamin D3 – protects the brain by controlling neurotransmitters and clearing amyloid plaques (found in Alzheimer’s Disease)
- Vitamin C – protects cells from the effects of free radicals
- Melatonin – facilitates sleep
Please be careful to work with your loved one’s primary care physician on vitamin supplementation. In many instances, these brain diseases are not the only health issues our loved ones are dealing with and some of the vitamins that might address dementia and Alzheimer’s Disease symptoms could negatively interact with other prescription medication for other health problems.
Our job as loving caregivers is to give the best care we are able to our loved ones, advocating for them, protecting them, making sure that everything that is being done is in their best interests.
We are there because we love them.
All the other participants in the caregiving journey are there for other reasons and those reasons may, intentionally or unintentionally, not consider what is best for our loved ones.
So it’s our job to make sure that we are the gatekeepers to the best care we are able to provide for the people we love. It’s a big responsibility, but, in my opinion, there is no greater gift we can give or be given in this life than to do this.